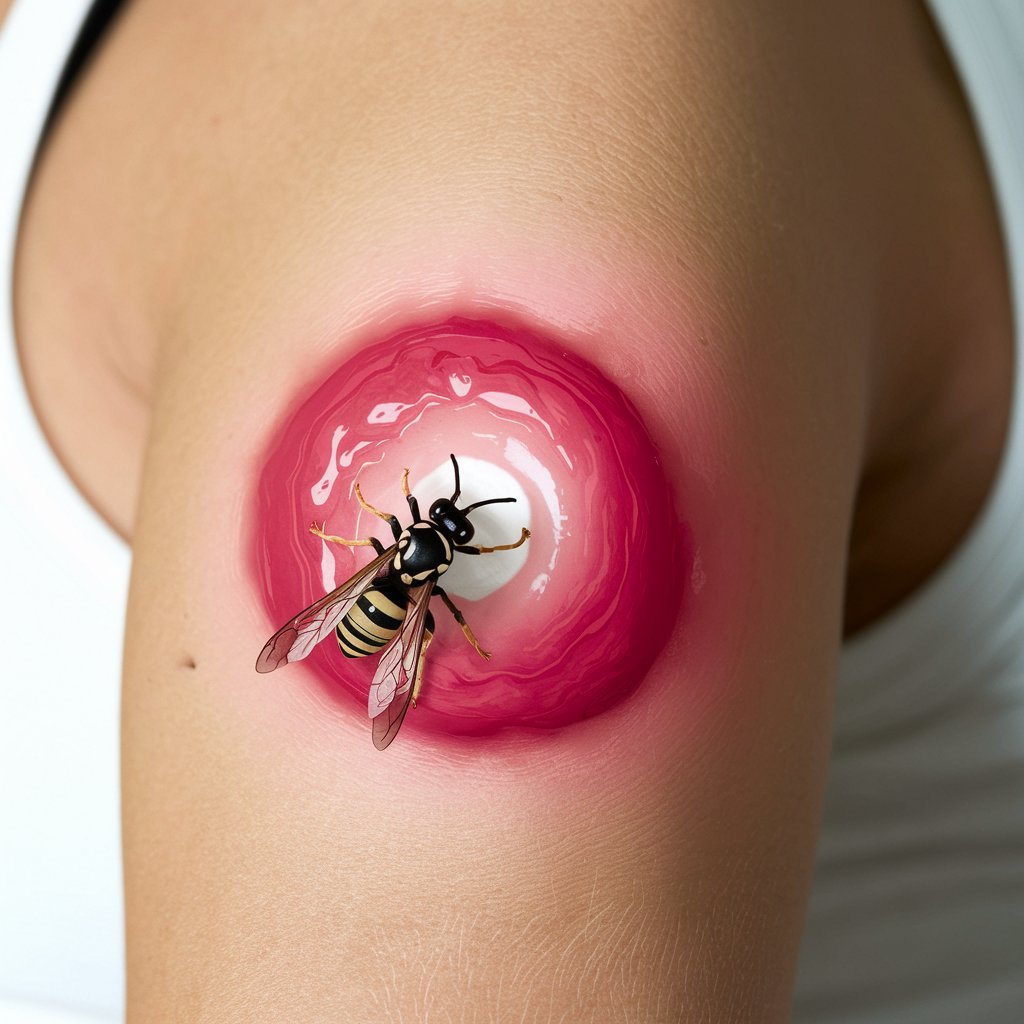
Most insect stings and bites are minor and a moderate skin reaction only. Among the most painful insect stings is that of bees, hornets, and wasps. Bees and hornets have barbed stingers, while wasps carry straight stingers, and both are used for defense purposes. In a wasp sting, the stinger is venomous and would be delivered upon a sting.
It is the venom, though, that causes the pain you feel later on. Some people suffer from very minor reactions, including itching, redness, and swelling. Others may face more serious reactions, such as rapid heart rate, diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. Among those allergic to wasp stings, anaphylaxis, or a serious reaction, can occur.
What does a sting look like?

The local reaction of a wasp sting may not look that different from many other insect bites or stings at first glance. Wasp stings are usually swollen and red and may feel warm to the touch. There is usually a red mark that looks like a pen prick in the center of the sting, Tania Mucci-Elliott, MD, a clinical instructor at the NYU Grossman School of Medicine, told Health.
Symptoms of Wasp Stings
Symptoms of a wasp sting depend on whether you are allergic to wasps. A mild reaction usually causes a pink or red, swollen patch of skin where the sting happened. You may feel itching or pain, which usually goes away within a few hours.
Some people have a more moderate reaction to wasp stings. Symptoms may include:
- Low blood pressure
- Diarrhea
- Nausea and vomiting
- Rapid heart rate
Stomach cramps
Do Wasps Leave Stingers in You?
Wasps, unlike bees, do not have a barbed stinger, which allows them to sting you multiple times. Therefore, wasps do not typically leave their stingers in your skin when they sting you. The more times a wasp stings you, the more venom transmits into your skin.
Anaphylaxis- Severe, potentially life-threatening allergic reaction from a wasp sting if you are allergic to wasps. Symptoms include:
- Collapse (from shock)
- Diarrhea
- Hives
- Nausea and vomiting
- Rapid heart rate
- Stomach cramps
- Swelling of the lips, mouth, throat, or tongue
- Trouble breathing
Complications
Mild wasp stings usually recover at home within one week. In contrast, anaphylaxis is an life-threatening reaction to a wasp sting and can prove fatal if left untreated.5

The danger of complications is more likely if you have allergies that fail to receive prompt treatment. You might be likely to develop a total body reaction if you’re stung often and the reactions get worse with each sting.
Wasp Sting Treatment
What should you do if you get stung by a wasp? You can treat a wasp sting at home as long as you do not develop a severe allergic reaction.
Remove the stinger: This is not usually the case, but carefully flick out the stinger without squeezing it if it’s lodged in your skin. Avoid squeezing the stinger, which may release additional venom.
Wash the site: Use water and gentle soap.
Apply a cold compress: This will help keep the swelling down. Keep the affected area still to keep the venom from spreading. Loosen any tight clothing and jewelry.
Reduce pain and itching with an OTC pain reliever, such as Advil (ibuprofen), for pain. Dr. Elliott suggested that the area be kept elevated and that the patient apply an analgesic, such as Cutter BiteMD Insect Bite Relief stick.
If you are stung by several wasps, you might want to visit your nearest urgent care center. A medical professional can assist you in removing several stingers from your skin if they are still lodged (which is unlikely).
When To Get Medical Care
Most people react mildly to a wasp sting. However, the possibility of a severe allergic reaction is not ruled out, especially if it is your first time being stung by a wasp.
Check with a healthcare provider if you feel something is off, even if you do not have any of the telltale signs of an allergic reaction.
- Abdominal and chest pain
- Anxiety
- Cough
- Diarrhea
- Feeling dizzy and lightheaded
- High-pitched breathing sounds
- Nausea and vomiting
- Swelling of the eyes, face, and tongue
- Trouble breathing and swallowing
- Unconsciousness
Prevention
It pays to just be aware of the places you spend time in, said Dr. Elliott: “Try to stay away from places that will have wasps, such as the eave of houses.”
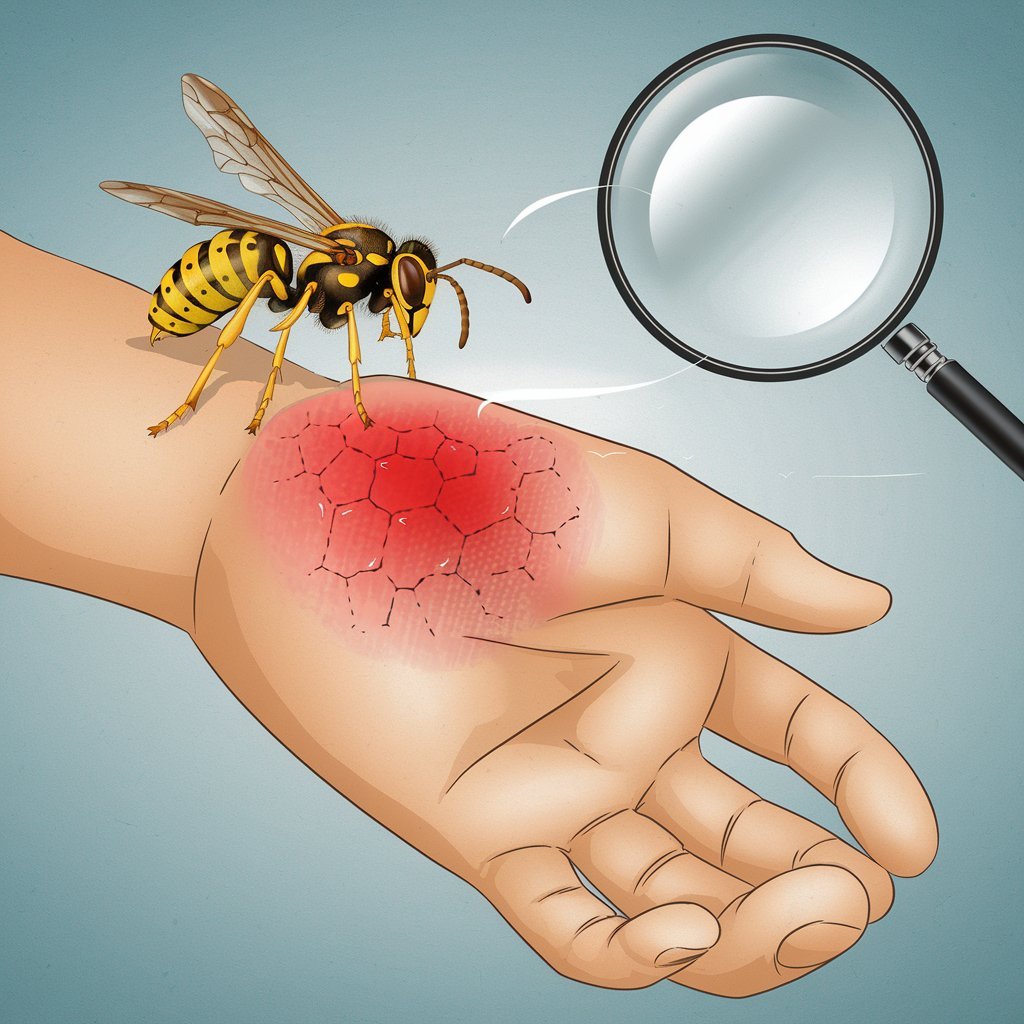
Do not wear bright colored clothing or perfumes if you’re going to areas where there are wasps.
Limit attracting wasps, as well as bees and hornets, if you are outdoors. Consider bringing covers for any food and drink items you bring with you.
Keep an eye out for wasps’ nests regularly if you constantly find the insects in your backyard. Never put your hands or feet in places where wasps typically hide, like hives and nests.
- If possible, do not provoke wasps by swatting at them.
- Garden using gloves.
- Wear shoes and socks while walking on grass.