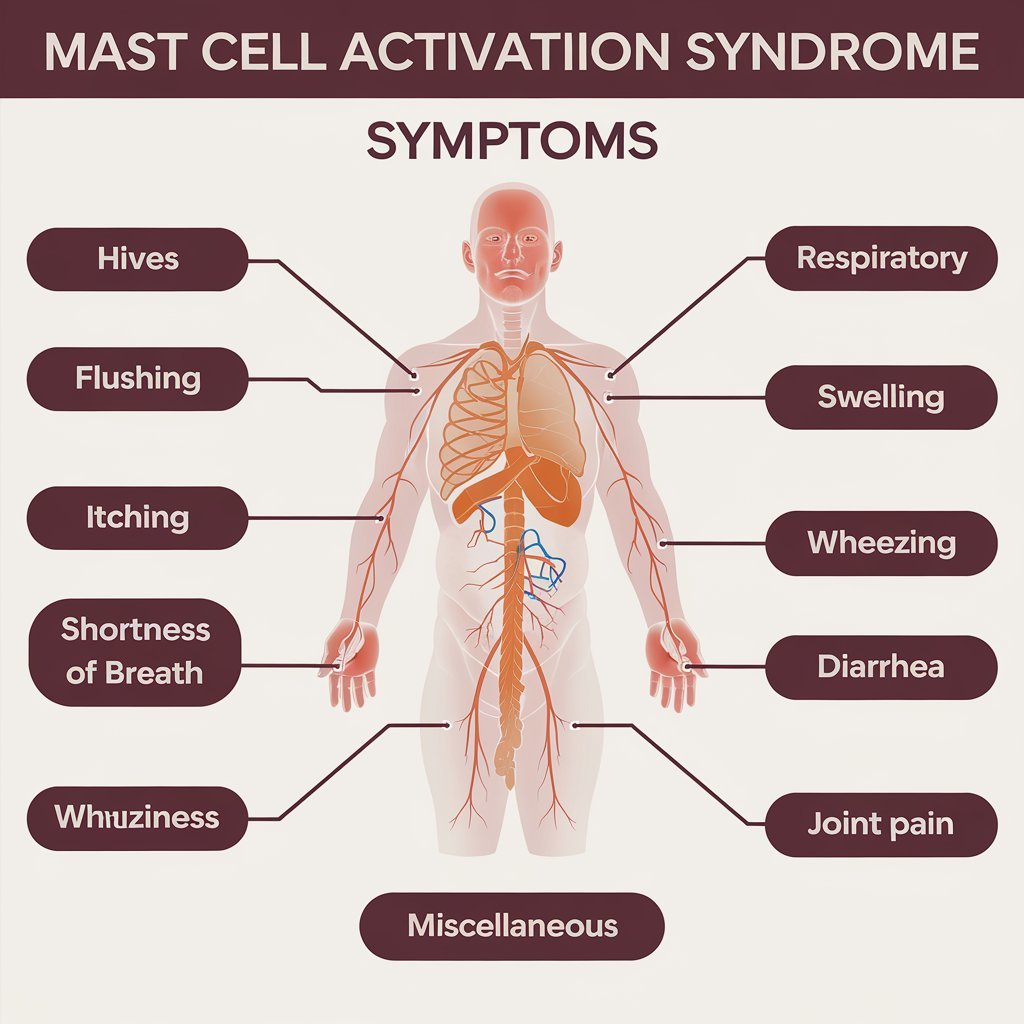
Mast cell activation syndrome is a condition wherein mast cells-a type of white blood cell responsible for playing an important role in the immune system-release excessive amounts of histamine and other inflammatory substances in response to normally harmless triggers, including foods, temperature changes, medications, stress, sunlight, or exercise.
Mast cells are found in tissues all over the body, including skin, gastrointestinal, cardiovascular, neurological, and respiratory systems. Normal mast cells detect and respond to infections, injuries, and other types of perils by releasing inflammatory mediators-the “mast cell mediators” that attack the threat and can promote healing.
With MCAS, mast cells are activated and mediate the frequent or excessive release of these mediators after one or more exposure to triggers that cause severe symptoms affecting many parts and systems in the body. The factors which contribute to episodes of MCAS and the severity of symptoms may vary from person to person.

The symptoms of MCAS may either be chronic and frequent or come and go in recurrent episodes. People suffering from MCAS might have mild symptoms over a prolonged duration before experiencing symptoms that increase in frequency and intensity.
Skin Symptoms
Skin has high concentrations of mast cells since it’s your body’s first line of defense against bacteria, viruses, and other environmental threats. Most patients with MCAS experience dermatologic symptoms that may include the following:
- Pruritis (itching): Itchiness can be intense and widespread
- Urticaria (hives): Raised, red welts on the skin’s surface
- Flushing: Sudden reddening of the face, neck, and chest due to dilated blood vessels and increased blood flow to the skin
- MedlinePlus. Blushing/flushing of the skin.
- Angioedema (swelling): Swelling under the skin around the lips, eyes, hands, feet, and throat
- Dermatographism: Scratching or pressing on the skin causes hives (raised, red welts)
Gastrointestinal Symptoms
Abdominal cramping or pain
- Bloating
- Diarrhea
- Cyclical or chronic nausea and vomiting
- Dyspepsia or indigestion
- Heartburn
- Dysphagia or difficulty swallowing
Respiratory Symptoms
MCAS symptoms that involve the respiratory system, which are lungs and airways, may include:
- Runny nose
- Nasal congestion
- Shortness of breath or breathlessness
- Wheezing sounds during breathing
- Cough
- Swollen throat
Cardiovascular Symptoms
Mast cell activation can cause effects on the heart and blood vessels, thus causing cardiovascular symptoms like:
- Tachycardia
- Heart palpitations
- Low blood pressure
- Fainting
- Chest pain or discomfort
Musculoskeletal Symptoms
MCAS can cause musculoskeletal symptoms that affect the musculoskeletal system, including muscles, bones, joints, ligaments, and tendons. Most people with MCAS experience these symptoms daily. They include:
- Joint pains
- Muscle pains
- Bone pains
- Osteoporosis or osteopenia; loss of bone mass
Neurological Signs and Symptoms
MCAS may affect the nervous system, thus causing a plethora of cognitive issues, psychiatric problems, and mood alterations, among others:
- Headaches
- Dyscognitive impairment, that is, dizziness, memory, or trouble concentrating
- and brain fogs
- Dizziness
- Anxiety, depression, or panic attacks
- Insomnia; inability to sleep or inability to maintain sleep at night
- Irritability or mood swings
- Neuropathy (nerve damage), which can be felt as numbness and tingling
- Tinnitus (ringing in the ears)
- Excessive daytime sleepiness
Genitourinary Symptoms
Genitourinary symptoms are symptoms which impact your urinary or reproductive organs. MCAS symptoms include;
- Frequent urination
- Urinary urgency is the sudden strong feeling to pass urine
- Discomfortful micturition
- Infertility
- Menorrhagia, the menstrual blood which lasts longer than seven days
- Dysmenorrhea: Pain during menstrual cramp during your monthly period
- Pregnancy which leads to loss
In men and individuals assigned male at birth, MCAS can lead to the following conditions:
- Prostatitis: inflamed, sore prostat
- Sexual dysfunction: inability to achieve or maintain an erection
Systemic (Bodywide) Symptoms
Generalized symptoms of MCAS that are not circumscribed to any single organ or body system are as follows.

- Fatigue
- Sweating
- Changes in appetite
- Mild, unintentional weight loss or gain
- Slowed wound healing time
- Weakness
MCAS and Anaphylaxis
Patients with MCAS are also at risk of having anaphylaxis—a severe allergic reaction. Symptoms of anaphylaxis develop suddenly and can quickly become severe and even fatal. Immediate medical treatment is necessary. The symptoms include the following:
- Abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting
- Chest tightness, heart palpitations
- Feeling difficulty in breathing or swallowing
- Nasal congestion
- Hives
- Slurred speech
- Facial swelling (including around the eyes and the tongue)
- Loss of consciousness
Symptoms in Children
MCAS occurs more frequently in adults than children; however, children are also not exempt. Children who develop symptoms at or near puberty are likely to have these symptoms into adulthood.
The symptoms of MCAS in children are similar to those in adults. If you suspect that your child may have MCAS see a doctor because a diagnosis can be obtained at this early time.
When to Reach a Healthcare Provider
MCAS symptoms differ with everyone, and often involve at least two of body systems in an individual case. Seek a health care provider immediately if you have the persistent or alarming symptoms, your symptoms affect multiple body systems, or the symptoms become distressing enough for your daily routines, work, and sleep.
- Persistent or recurrent cutaneous symptoms which may include any of the following; itching, hives, flushing, swelling
- Ongoing gastrointestinal issues such as abdominal tenderness, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or constipation
- Trouble breathing or wheezing or coughing chronically
- Headaches, brain fog, or dizziness
- Frequent urination or urinary urgency
Seek medical emergency care if you have symptoms of anaphylaxis, such as:
- Sudden, severe swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat
- Wheezing, shortness of breath, or trouble breathing that rapidly worsens
- Fainting or loss of consciousness
- Chest pain, chest tightness, or rapid heart rate (over 100 beats per minute)
- Sudden, severe diarrhea, nausea, or vomiting
A Quick Review
Mast cell activation syndrome, abbreviated as MCAS, is a disorder characterized by excessive release of inflammatory chemicals by mast cells due to a normally innocuous stimulus. Patients with MCAS may exhibit manifestations in the skin, gastrointestinal, respiratory, cardiovascular, musculoskeletal, neurological, and genitourinary systems.
Symptoms can range from one patient to another; some symptoms reported are itching, hives, shortness of breath, problems in the gastrointestinal system, lethargy and confusion. Go to a doctor in case you face any chronic symptoms of MCAS. The better management of such symptoms with the initial diagnosis can actually enhance the quality of life.