If you often find that right after eating specific food items, for a few minutes, your roof of mouth gets itchy, you could have oral allergy syndrome, which is also called pollen food allergy syndrome. OAS is the most prevalent food allergy affecting adults.
OAS is characterized by mild itching and swelling in your mouth, lips, tongue, or throat. Most people feel the symptoms start a few minutes after eating a certain food but sometimes it can take up to a half hour.
Normally, OAS occurs in individuals allergic to pollen. There are proteins in some foods that resemble proteins in pollen, and your immune system gets confused and mounts an attack. Once the food makes contact with your mouth, an immune response happens. OAS is usually a mild allergic reaction, but in rare cases it can be serious.

OAS usually happens when you’re experiencing allergic rhinitis, also called hay fever or just seasonal allergies. Allergies happen because your body releases histamine, an immune system chemical that causes symptoms of allergies. If your immune system is already geared up from pollen, eating certain foods that contain similar proteins can also make your mouth and throat feel itchy.
Some foods are more likely to cause OAS than others. Canned versions of OAS-eliciting foods can limit your body’s reaction.
Apples
Apples and birch tree pollen share similar proteins so that if one has an allergy to birch trees they may also be sensitive to apples perhaps more so with certain varieties than others. Birch trees are found in all 50 states and tend to bloom in the first months of the year.
Some people feel that Granny Smith apples itch their mouth more than any other variety of apples, but it is not always the case. Fuji may not be as bothersome for many, but most individuals with OAS toward apples will either avoid all or find a variety that doesn’t bother them nearly as much.
Melons
Millions of people suffer from ragweed allergy, the weed that sprouts in all 50 states. Because proteins in the pollen of ragweed are similar to proteins in melons, crossover reaction can take place. There is a specific itchy roof of mouth by cantaloupe, honeydew and especially watermelon for seasonal allergies.
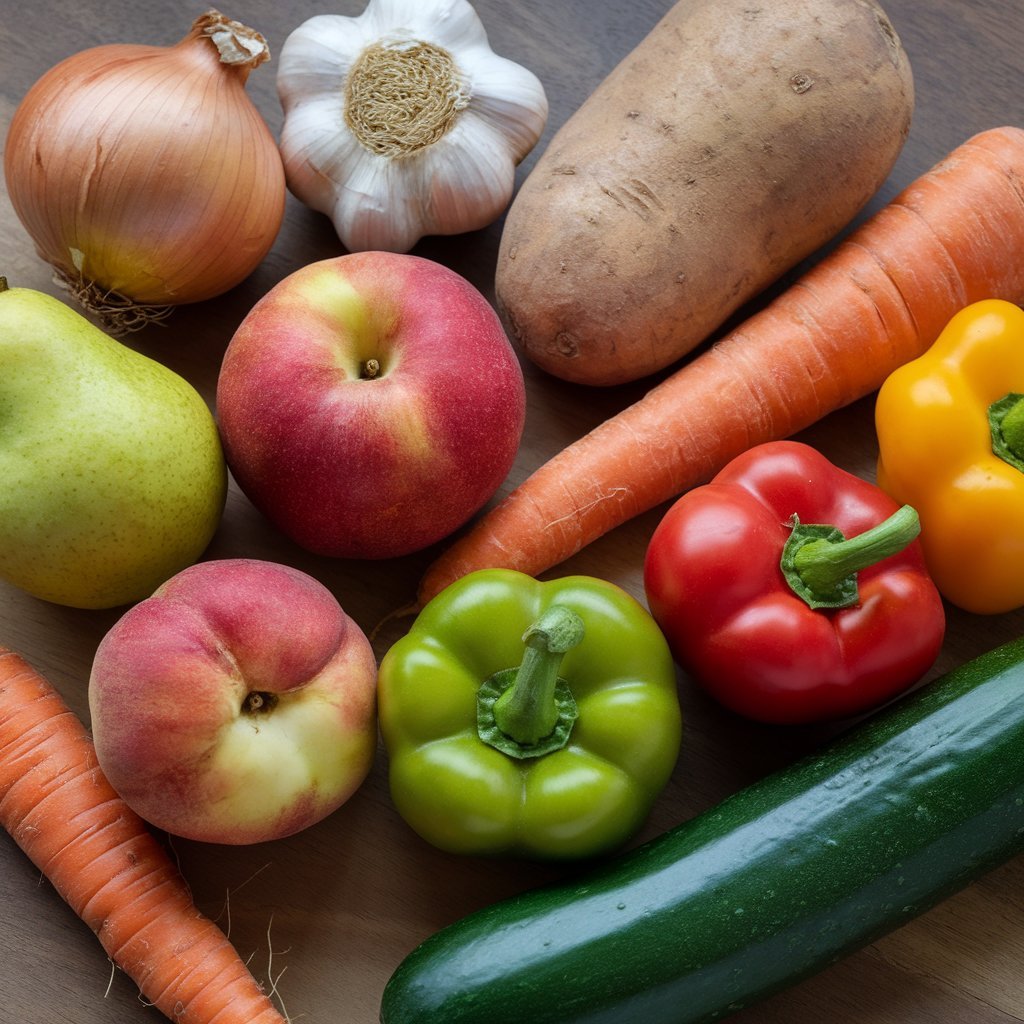

Watermelon can also cause an itchy roof of mouth for people with grass allergies, like orchard grass and Timothy grass. If you have hay fever from ragweed or grasses—and especially if you have both—it may be best to avoid watermelon.
Zucchini
Ragweed pollen and zucchini have similar proteins, so if you’re allergic to ragweed, zucchini may also pose a problem. Zucchini is usually eaten cooked, so if your allergy is mild, zucchini may still be okay to eat as the cooking process breaks down the protein.
The allergen-producing proteins are often in higher concentrations in the peel, so peeling the zucchini first may help reduce your allergic reaction or help you avoid symptoms altogether.
Bell Peppers
The different varieties of bell peppers include the normal green, red, orange, yellow, white, and even purple ones. The good news is that despite all the variations in color, there is a similarity between all the proteins. The proteins resemble the common weed known as mugwort and have a tendency to make an allergic seasonal mugwort person feel itchy and swollen.
Peeling a fruit or vegetable before eating it can often cut down on the allergic reaction it may induce, but bell peppers are hard to peel. However, they can be cooked, which should reduce or inhibit the reaction.
Oranges
Oranges contain similar proteins to grass pollens and can induce symptoms of allergic rhinitis. This may happen with different types of oranges, such as clementines, tangerines, mandarins, blood oranges, and others.
While OAS can occur with any type of plant food, oranges are the citrus fruit most likely to provoke symptoms. Lemons, limes, and grapefruit, other citrus fruits, are generally not as irritating. Most of the proteins are located in the peel, which typically is not eaten. However, some recipes incorporate orange peel. Be on your guard for these recipes, because the peel provokes a much greater reaction.
Cruciferous vegetables
Scientists have recently been exploring the cancer-fighting compounds within cruciferous vegetables such as broccoli, cauliflower, and cabbage. Unfortunately, because the proteins of cruciferous vegetables are so similar to those of mugwort pollen proteins, they cause allergic reactions in individuals with sensitivities to mugwort pollen.
The good news is that most of the protein is broken down by cooking. If raw cabbage, cauliflower, broccoli, or any other cruciferous vegetable causes your mouth to itch, try cooking them. The cooking process denatures the protein, breaking it down so your immune system may not recognize it.
White Potatoes
Both ragweed and grass pollen proteins are similar enough to those in white potatoes, so if you’re allergic to ragweed and grass pollen, eating white potatoes can cause your immune system to react.
However, thankfully, potatoes don’t usually cause a problem because they are not eaten raw often. Cooking potatoes destroy enough of the protein that it causes less of an allergic reaction. Peeling the potato can even be more helpful. Although most of the nutrients are in the skin, by peeling it, you are removing most of the proteins that cause allergic reactions. Some people get itchy hands that are red and swell when they peel white potatoes.
Garlic and Onion
Both garlic and onions have proteins that are similar to mugwort pollen. If your rhinitis is caused by mugwort, you may also feel an itchy mouth when eating garlic and onion.
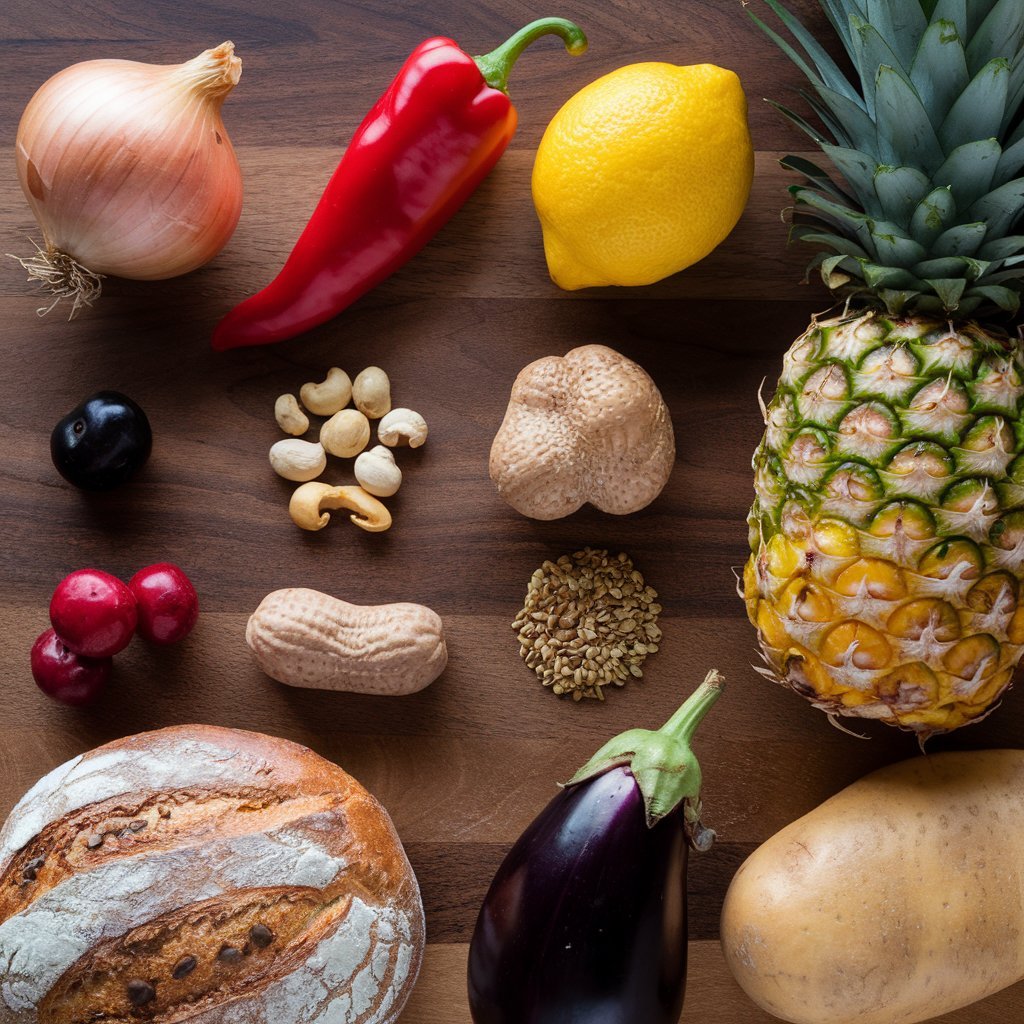

Cooking both garlic and onion can also help since the cooking denatures the proteins to make them ineffective. If you have a mild OAS, you can begin by trying out these vegetables once they are cooked to see whether you can still tolerate them. Allium vegetables, such as garlic and onions, are tied to immense health benefits and include plant compounds with anti-cancer properties, lowering inflammation, and improving metabolic well-being.
Bananas
Fruits commonly grown in tropical environments, such as bananas, can also cause OAS symptoms. The protein in bananas is similar to the protein in ragweed, causing an immune system reaction in those with seasonal ragweed allergies.
Most of the protein resides in the peel, which is good, since people do not eat the peels. Banana peels are edible, but rarely. Sadly enough, drying the banana and then eating it as a chip does not reduce the amount of protein it contains.
Tomatoes
If you have seasonal allergies to birch, cypress, cedar, or grass, you might react to tomatoes. All these plants share the same proteins, and eating raw tomatoes can provoke an immune response – an itchy mouth or a runny nose, for example.
Tomatoes and other red vegetables and fruits are replete with a carotenoid known as lycopene, with multiple health benefits. This antioxidant helps to cut oxidative stress in association with type 2 diabetes. Try cooking tomatoes to gain health benefits but at the same time reduce your chance of reacting to them.
Pineapples
If you live in an area where oak, mesquite, and ash trees thrive, and you have seasonal allergies to their pollen, you can also react to pineapples. Like the others on this list, they have very similar proteins that cause immune system reactions. Studies show that pineapple is a common source of OAS in children.
Pineapples have also been noted to cause a burning sensation on your tongue, which is very different from OAS. The sensation is caused by bromelain, a collection of enzymes found in the pineapple. These enzymes break down proteins and cause soreness of the tongue
Spices
It is not just fruits and vegetables that can cause OAS. Certain spices have the same proteins as mugwort and produce the same itchy and swollen reaction. Among these spices are aniseed, coriander, fennel, parsley, caraway, and black pepper.
If you enjoy using these spices but they cause itchiness, try using dried spices instead of fresh, raw spices. Avoiding the raw version of any of these foods can help cut down on the amount of protein that you’re ingesting.
Why do some types of food make your mouth itchy?
Many different types of fruits and vegetables contain proteins that are nearly identical to proteins found in pollen. Your immune system can become confused by their similarity, and begin to produce histamines to fight the allergen. If you’re already experiencing hay fever symptoms from pollen in the air, eating food with a similar protein can make your symptoms worse. This is called cross-reactivity.
It is, however important to note that itchiness after consuming nuts may indicate a more severe allergic reaction. Some nuts and legumes such as soybeans, peanuts, hazelnuts, and almonds may be related to a birch pollen allergy; however, itchy feeling can also mean something more severe.
Contact an allergist or immunologist if you notice itching of the mouth or throat soon after consuming nuts, such as peanuts. Nut allergies are severe and should always be consulted with a health care provider.